

Old cathode ray tube on white background. To commemorate the discovery of the electron by J. Cathode Ray Tube Diagram In electric magnetic fields (J J Thomson experiment) Stock Illustration.He observed that a beam of particles, called cathode rays, was emitted. As a result of his work, Thomson proposed a completely new model of the atom (Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model) that one of his students, Ernest Rutherford, would improve upon 10 years later.Ĭlick and drag the cursor to change the intensity of the voltage applied between the plates. Thomson passed an electric current through a glass tube containing gas at low pressure. He zapped atoms with electricity and observed that negatively charged particles were removed He reasoned that atoms consisted of subatomic particles, electrons that were negatively charged particles. Thomson, a British physicist, conducted the cathode ray experiment. Cathode ray tube (CRT) - a vacuum-sealed tube in which electrons flow from the cathode. This apparatus constitutes the first particle accelerator. Previously, atoms were known to be indivisible, but in 1897, J. Thomson - an English physicist who used cathode rays to discover the existence of electrons in 1897. Cathode Ray Tube 16 - light shined on a pinwheel inside a CRT does not cause the pinwheel to move. Cathode Ray Tube 14 - cathode rays cast a shadow behind a Maltese Cross. Thomson, in 1897, isolated a new elementary particle carrying a negative charge – the electron. Cathode Ray Tube 12 provides evidence that cathode rays are not visible to human eyes. The very intense electric field that results from this accelerates the few ions present in the tube which, via collisions, ionize other particles. The lower the pressure, the more the electrons thus liberated and accelerated travel great distances until they strike the screen at the opposite end of the tube.īy studying the deviation of this beam, J. A high voltage (between 10 and 100 kV) is applied between two electrodes. Thomson’s second experiment involving the deviation of an electron beam in a vacuum tube, called a Crookes Tube.Ī partial vacuum (less than 10 -6 atm) is maintained in the tube. It does not store any personal data.This animation describes J. The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies.

The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin.
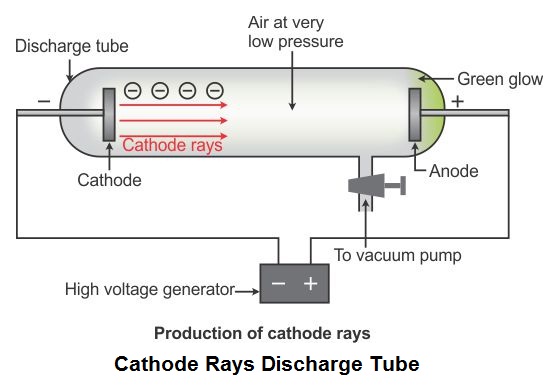
The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The arrangement used was as follows:-Two coaxial cylinders (fig. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously.
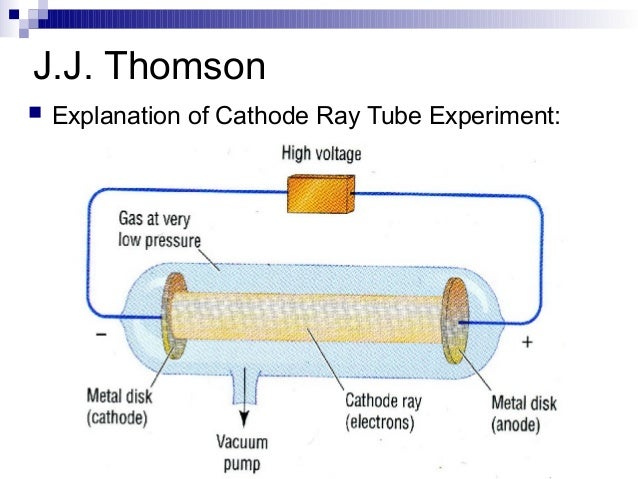
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
